
All posts by admin


White kidney bean Extract
Botanical name: Phaseolus vulgaris
Family: Fabaceae
Common Name: White kidney bean, Common bean
Part used: Seed

Moringa Leaf
Botanical name: Moringa oleifera
Family: Moringaceae
Common Name: Drumstick, Horse-radish
Part used: Fruit, Leaf

Boswellia serrata Extract
Botanical name: Boswellia serrata
Family: Burseraceae
Common Name: Salai guggal, frankincense
Part used: oleo-gum-resin
Category: Weight Management

Triphala

Licorice

GUDUCHI (TINOSPORA CORDIFOLIA)

FENUGREEK

Cinnamomum

Papaya Leaf

BLACK PEPPER
Kumar Enterprises Products revamps corporate website
Kumar Enterprises Products revamps corporate website More Details >

Slide 1
Greening Global Health Care!

Slide 2
We Care Healthy Families !

Slide 6
Kumar Enterprises Products is an ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company
Kumar Enterprises Products is an ISO 9001:2008 Certified Company

Slide 3
Contract Manufacturing
Kumar Enterprises Products offers complete contract manufacturing and packaging services. Kumar Enterprises’ streamlined contract manufacturing services help you with each step of the process, including planning, formulation, production, labeling and packaging.
Kumar Enterprises’ state-of-the-art manufacturing facility uses the most advance technology in producing supplements and other nutritional and beauty products. All manufacturing and testing is conducted in GMP-certified facilities.
Kumar Enterprises team will provide you with a free, no obligation quote for your contract manufacturing needs within 48 hours. Your dedicated account executive can help you with bulk, private labeled, or even custom formulation orders.

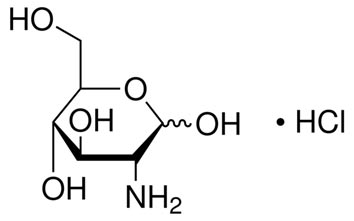
Glucosamine Hydrochloride
One complementary medication that has been investigated for the treatment of OA is glucosamine. Glucosamine is a derivative of cellular glucose metabolism. It is also a component of glycosaminoglycans and proteoglycans of the cartilage matrix covering the ends of bones and hyaluronic acid which is a part of synovial fluid within the joint. The primary source of exogenous glucosamine is the exoskeleton of shellfish and exists in primarily two formulations, glucosamine hydrochloride (HCl) and glucosamine sulfate. Glucosamine sulfate requires compound stabilizers in the form of salts and has 74% purity. Glucosamine HCl lacks the sulfate group and has 99% purity. Therefore, glucosamine HCl in a dosage of 1,500 mg equals a dosage of 2,608 mg of glucosamine sulfate. Glucosamine is readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract with oral administration, rapidly undergoes metabolism via the liver and the first pass effect, and is eliminated through the feces and urine. Peak levels are in about 8 hours after oral ingestion primarily due to about 90% protein binding.
| Chemical Structure |
 |
The mechanism of action of glucosamine in humans is unknown. Because glucosamine is a part of the cartilage matrix in joint tissues, it has been theorized for many years that its administration could affect symptomatic relief for OA sufferers by supplying the components for cartilage repair and thus improve pain and disability. More recently, however, it has been demonstrated in animal models that glucosamine has an anti-inflammatory effect via the reduction of nuclear factor kappa beta induced by interleukin-1 (IL-1). A few studies in humans have revealed that glucosamine HCl reduces IL-1 stimulated production of catabolic enzymes and inflammatory markers such as prostaglandin E2 by chondrocyte and synovial cells harvested from surgical specimens removed from patients with OA.

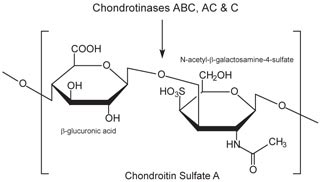
Chondroitin Sulphate
Chondroitin sulfate is a sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) composed of a chain of alternating sugars (N-acetylgalactosamine and glucuronic acid).
Chondroitin sulfate is an important structural component of cartilage and provides much of its resistance to compression. Along with glucosamine, chondroitin sulfate has become a widely used dietary supplement for treatment of osteoarthritis.
| Chemical Structure |
 |
Chondroitin sulfate plays a central role in various biological processes, such as the function and elasticity of the articular cartilage, inflammation, cell adhesion, proliferation and differentiation. Number of commercial applications increased, due to its high biocompatibility, mainly in the engineering of biological tissues associated with the processes of bone repair, cartilage and cutaneous wound.

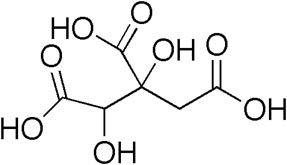
Garcinia Cambogia Extract
Botanical name: Garcinia cambogia
Family: Guttiferae
Common Name: Garcinia, Malabar Tamarind
Part used: Fruit rind
Phytochemicals: Hydroxycitric acid (HCA)
| Chemical Structure | Specifications |
 |
|

Turmeric Extract
Botanical name : Garcinia cambogia
Family : Zingiberaceae
Common Name : Turmeric
Part used : Rhizome
| Specifications |
|

Salacia Extract
Botanical name : Salacia reticulata
Family : Hippocrateacaea
Common Name : Salacia, Kotalahimbatu, Saptarangi
Part used : Root and stem bark
Phytochemicals : Tannins and Triterpenes
| Specifications |
|
Category : Blood Sugar Support, Weight Management

Amla
Botanical name : Emblica officinalis
Family : Euphorbiaceae
Common Name : Amla, amlaki, Indian Gooseberry
Part used : Fruit
Phytochemicals : Tannins
| Specifications |
|
Category : Antioxidant, General Tonic
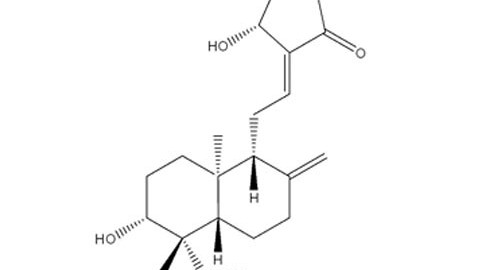
Andrographolide 95%
CAS number: 5508-58-7
Plant source: Andrographis paniculata
Andrographolide is a labdane diterpenoid that is the main bioactive component of the medicinal plant Andrographis paniculata. Andrographolide is an extremely bitter substance extracted from the leaves of A. paniculata.
Andrographolide is used experimentally in different areas of research including cell signaling, immunomodulation, and stroke.
Colchicine 98%
CAS number: 64-86-8
Plant source: Colchicum autumnale
Colchicine is a medication most commonly used to treat gout. It is extracted from plants of the genus Colchicum (autumn crocus, Colchicum autumnale, also known as “meadow saffron”).
Colchicine is an alternative for those unable to tolerate NSAIDs in gout
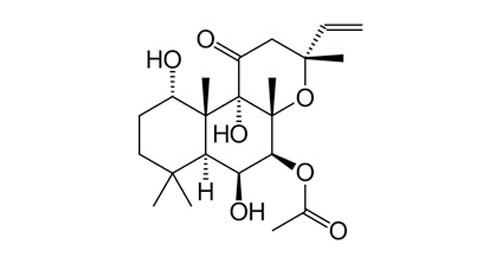
Forskolin 95% and 97%
CAS number: 66428-89-5
Plant source: Coleus forskohlii
Forskolin (also called Coleonol) is a labdane diterpene that is produced by the Indian Coleus plant (Coleus forskohlii). Forskolin is commonly used to raise levels of cyclic AMP (cAMP) in the study and research of cell physiology. Forskolin activates the enzyme adenylyl cyclase and increases intracellular levels of cAMP.
Forskolin is also used in cosmetic formulations.
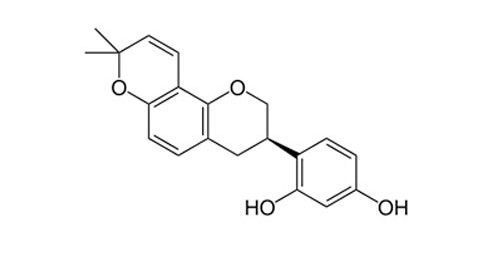
Glabridin 95%
CAS number: 59870-68-7
Plant source: Glycyrrhiza glabra
Glabridin (is a chemical compound that is found in the root extract of licorice (Glycyrrhiza glabra). Glabridin is an isoflavane, a type of isoflavonoid. This product is part of a larger family of plant-derived molecules, the natural phenols.
It is used as an ingredient in cosmetics and is listed in International Nomenclature of Cosmetic Ingredients (INCI).
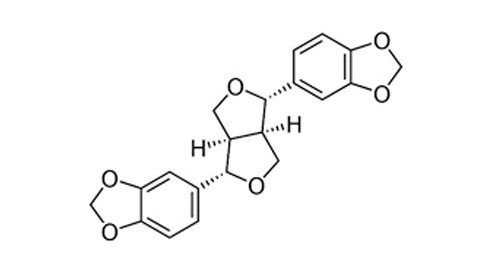
Sesamin 90%, 95%
CAS number: 607-80-7
Plant source: Sesamum indicum
Sesamin is a lignan isolated from the sesame oil. It has been used as a dietary fat-reduction supplement, Sesamin and sesamolin are minor components of sesame oil, on average comprising only 0.14% of the oil by mass
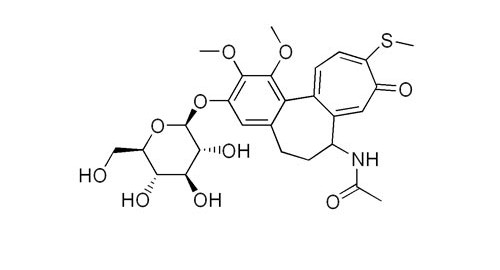
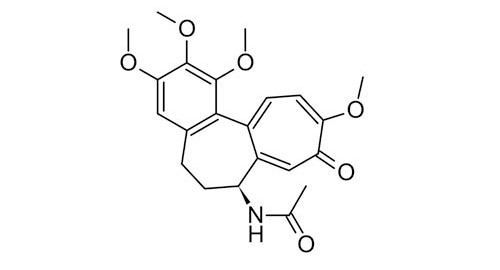
Thiocolchicoside 99%
CAS number: 602-41-5
Plant source: Gloriosa superba
Thiocolchicoside, a semisynthetic colchicoside from the plant Gloriosa superba, is a muscle relaxant and used to treat rheumatologic and orthopedic disorders because of its analgesic and anti-inflammatory mechanisms.

Garcinia Extract
Botanical name: Garcinia cambogia
Family: Guttiferae
Common Name: Garcinia, Malabar Tamarind
Part used: Fruit rind
Category: Weight Management

Turmeric Extract
Botanical name: Curcuma longa
Family: Zingiberaceae
Common Name: Turmeric
Part used: Rhizome

Bacopa Extract
Botanical name: Bacopa monniera
Family: Scrophulariaceae
Common Name: Brahmi, Water Hyssop
Part used: Leaf
Category: Memory and Brain Health
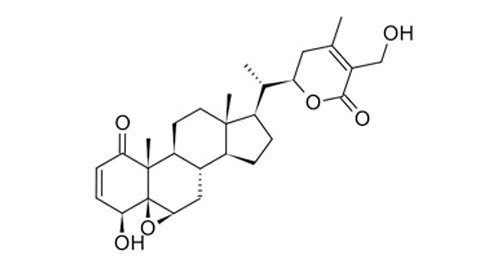
WWithaferin – A 95%
CAS number : 5119-48-2
Plant source : Withania somnifera
Withaferin A is a steroidal lactone isolated from Winter cherry (Withania somnifera) and is the first member of the withanolides to be discovered. Withaferin A is a potent inhibitor of angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels). Withaferin A inhibits both NF-κB and Sp1 Transcription factor activity. Withaferin A also down regulates VEGF gene expression and can affect calcium signaling.

Triphala Extract
Botanical name: Terminalia chebula, Terminalia bellerica, Emblica officinalis
Triphala is a combination of three very powerful fruits that are known to possess intensive health benefits. Triphala is widely used in Ayurveda medicine and the three fruits that comprise it are Amla, Myrobalan, and Belleric Myrobalan.
Triphala has many benefits and it includes protection and enhancement of the functions of the body organs such as the eyes, skin, and heart. It can also cleanse the body so that energy is channeled better and more intensively. In its most natural form, triphala is known as the most effective combination of herbs that can cleanse the colon, keep the liver healthy, and flush out body toxins. It effectively regulates the functions of the digestive system, while enhancing the strength of the immune system, lungs, urinary tract, and the muscles.

Slide 4

Slide 5
Sate of the Art Manufacturing Facility!

Slide 7
National Award from Government of India.
National Award from Government of India.

Holy Basil Extract
Botanical name: Ocimum tenuiflorum
Family: Lamiaceae
Common Name: Holy Basil, Tulsi
Part used: Leaves
Category: Stress Management

Amla Extract
Botanical name: Emblica officinalis
Family: Euphorbiaceae
Common Name: Amla, amlaki, Indian Gooseberry
Part used: Fruit
Category: Antioxidant, General Tonic

Garcinia
Botanical name: Garcinia cambogia
Family: Guttiferae
Common Name: Garcinia, Malabar Tamarind
Part used: Fruit rind
Phytochemicals: Hydroxycitric acid (HCA)
| Chemical Structure | Specifications |
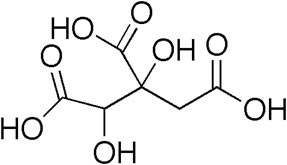 |
www.garsol.in |
Category: Weight Management

Turmeric
Botanical name: Curcuma longa
Family: Zingiberaceae
Common Name: Turmeric
Part used: Rhizome
Phytochemicals: Curcuminoids, Turmerones
| Chemical Structure | Specifications |
|
Ar – Turmerone
|
|

Lutein (Marigold)
Botanical name: Tagetes erecta
Family: Asteraceae
Common Name: Marigold
Part used: Flower petals
Phytochemicals: Lutein and Zeaxanthin
| Chemical Structure |
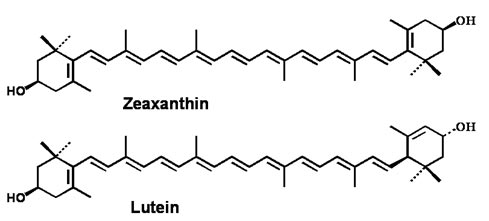 |
| Specifications |
|
Category: Eye Health

Sesame
Botanical name: Sesamum indicum
Family: Pedaliaceae
Common Name: Sesame
Part used: Seed
Phytochemicals: Sesamin, Sesamolin
| Chemical Structure |
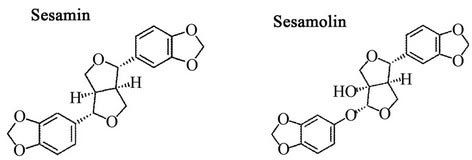 |
| Specifications |
| 70% Sesamin complex, 95% Sesamin |
Category: Cholesterol Management, Blood Sugar Support, Weight Management

Salacia
Salacia Extract
Botanical name: Salacia reticulata
Family: Hippocrateacaea
Common Name: Salacia, Kotalahimbatu, Saptarangi
Part used: Root and stem bark
Phytochemicals: Tannins and Triterpenes
| Specifications |
|
Category: Blood Sugar Support, Weight Management

Gymnema
Botanical name: Gymnema sylvestrae
Family: Asclepiadaceae
Common Name: Gymnema, Madhunashini
Part used: Leaves
Phytochemicals: Gymnemic acids and Gymnemagenin
| Chemical Structure |
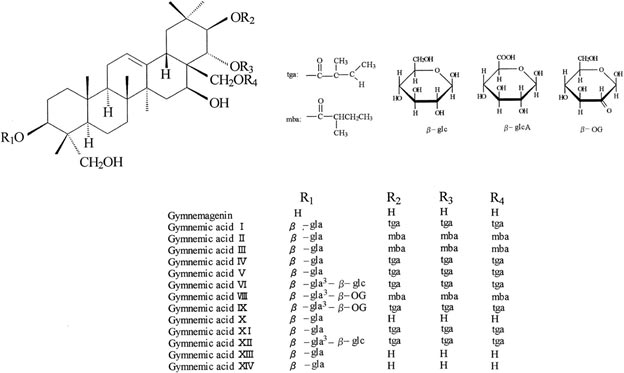 |
| Specifications |
|
Category: Blood Sugar Management

Green coffee bean
Botanical name: Coffea arabica
Family: Rubiaceae
Common Name: Coffee beans
Part used: Seeds
Phytochemicals: Chlorogenic acids
| Chemical Structure |
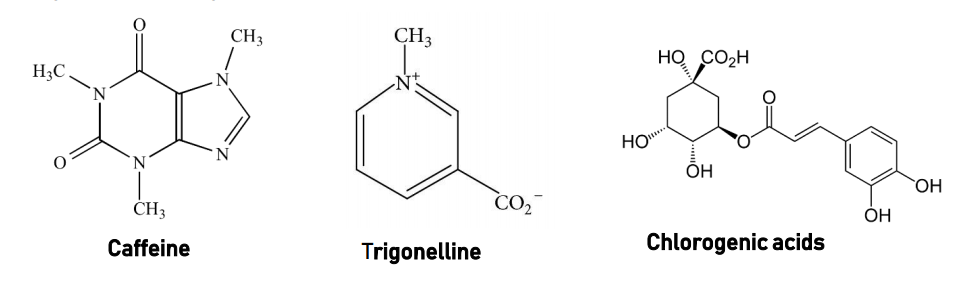 |
| Specifications |
|
Category: Weight Management, Blood Sugar Support

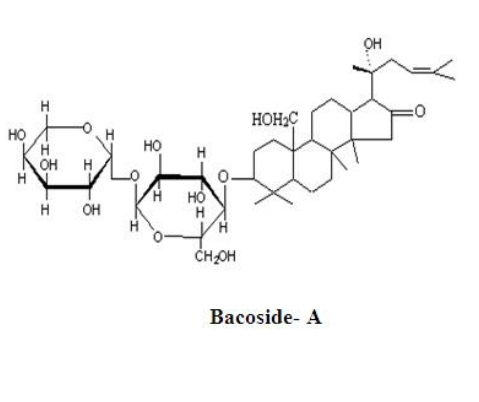
Bacopa
Botanical name: Bacopa monniera
Family: Scrophulariaceae
Common Name: Brahmi, Water Hyssop
Part used: Leaf
Phytochemicals: Bacopaside I, Bacoside A3, Bacopaside II, Jujubogenin isomer of bacopasaponin C, Bacopasaponin C
| Chemical Structure | |
|
|
|
| Specifications |
www.bacosmart.com |
Category: Memory and Brain Health

Bitter melon
Botanical name: Momordica charantia
Family: Cucurbitaceae
Common Name: Bitter guard, Bitter melon
Part used: Fruit
Phytochemicals: Bitters
| Specifications |
| 5% total bitters |
Category: Weight Management, Blood Sugar Support






 Herbal Extracts
Herbal Extracts Organic Ingredients
Organic Ingredients Water Soluble Ingredients
Water Soluble Ingredients Contract Manufacturing
Contract Manufacturing